Both of them are the optional values of enctype where the <form> element specifies the content type used to encode the form data set for submission to the server. There are three choices:
- application/x-www-form-urlencoded (default)
- multipart/form-data
- text/plain
application/x-www-form-urlencoded
- Just like a querystring:
name=John+Smith&age=27; - Each character that cannot be expressed using the selected character encoding, replacing the character by a string like
&#xxxx;wherexxxxmeans the Unicode code point of the character in base 10. (NCR); - Replace
0x20(space) the byte by+; - Leave characters match
/[\*\-\.0-9A-Z_a-z]/(alphanumeric) as is; - Otherwise, replace the byte (non-alphanumeric) by
%HH(must be two) whereHHmeans the uppsercase ASCII hex digits representing the byte.
multipart/form-data
Talk is cheap, show you the code:
|
|
The corresponding HTTP request would like this:
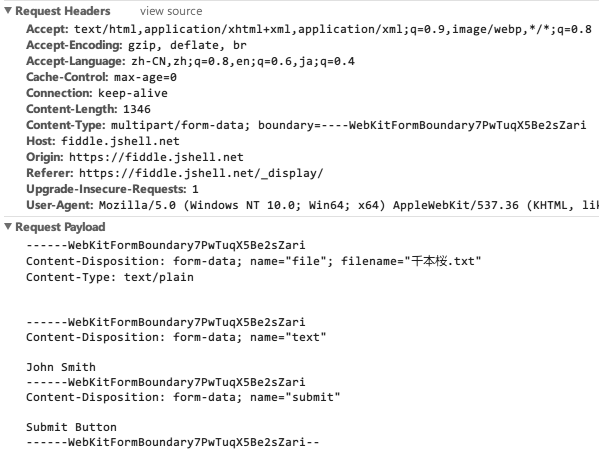
The boundary in the Content-Type works just like the & in querystring, but its value shall never appear in the entries (key and value).
The name in the Content-Disposition is the same as the entry’s name.
text/plain
Do not use.
Payloads using the text/plain format are intended to be human readable. They are not reliably interpretable by computer, as the format is ambiguous (for example, there is no way to distinguish a literal newline in a value from the newline at the end of the value).
Application
If you have binary (non-alphanumeric) data (or a significantly sized payload) to transmit, use
multipart/form-data. Otherwise, useapplication/x-www-form-urlencoded.
BTW, if you are using ajax, there are more choices for you. Like application/json, application/xml…